How to Cite AI in MLA Format
Need to know how to acknowledge the use of AI? Here, we cover citing AI-generated material in your academic work in MLA format.

Knowing how to use AI in the classroom is new for everyone, but one essential task to understand is how to cite AI in an essay. Citation shows the intellectual path you took to the arguments you’re making and is critical to avoid AI plagiarism. The rules around citations are evolving, but major style guides such as MLA have provided some initial guidance.
While Brown University provides this useful and concise overview, here, we want to dive specifically into guidance and examples around how to cite AI-generated material in your academic work in MLA format: when to cite AI, how to format full citations, and how to cite AI-generated images.
What does it mean to cite AI?
The rules for AI use in the classroom still vary across institutions and classrooms, which is why the very first thing you need to do is check the generative AI policies for your course. Only after doing that will you know how to cite AI tools appropriately for your assignment. However, a general rule to bear in mind is if in doubt, cite (don’t hide) AI use.
As Kimberly Munko, Adjunct Faculty at South College, says, “The academic community expects honesty. If you used AI for something like grammar help, you should include an AI disclosure, even if no one could detect it. Being open about it builds trust.”
While the frameworks will only continue to get updated, there are two principles that apply across the board: always cite AI outputs when you use them directly, and remember that generative AI can invent citations entirely, also known as ‘hallucitations’ (although with GPTZero’s Hallucination detector tool, you can detect potentially misleading claims).
Why do we cite AI?
Citing AI matters for the same reasons you cite any book or article: it keeps your work honest and helps readers understand your thinking process.
Munko adds, “Many institutions view disclosure of AI use as part of academic integrity. Graduate students are held to higher standards, so requiring disclosure from them is consistent with current expectations. Explaining how AI was used (e.g., editing, brainstorming, translation, citation formatting) aligns with emerging best practices.”
With more teachers using AI detectors in their workflows, being open about AI use matters: tools like GPTZero helps show where AI might appear in your writing.
Citing AI also encourages you to take a second to consider the actual quality of what the tool produced and whether its suggestions are accurate, which strengthens your AI literacy. It also builds your skills in explaining how those suggestions shaped your thinking.
Let’s assume you’re writing an essay on “How should judges be appointed?” If you ask ChatGPT to outline judicial appointment systems and use part of that explanation in your essay, the AI has become a source, and your instructor should be shown that.
When should you cite ChatGPT and AI in MLA?
You should cite AI in MLA when the tool’s output becomes part of the work your reader sees. If you include AI-generated text, paraphrased ideas, images, or data, then the tool should be credited just like any other material. MLA notes that if you use AI behind the scenes (like for translation or editing), it’s good practice to mention this somewhere in your paper, even though the details won’t appear in your Works Cited list.
MLA style is designed to be more flexible than APA or Chicago, and you’re encouraged to follow the guidelines to fit the situation rather than blindly adhere to a strict template. Since AI-generated content doesn’t have a human author, MLA treats it as a source without one. Instead of an author name, you use a brief description (often an abbreviated version of your prompt) both in your Works Cited entry and in your in-text citations.
If the AI platform lets you create a shareable link to the chat transcript, MLA recommends including that link instead of the tool’s generic homepage. This gives your reader a stronger view of the exchange that produced the AI-generated content.
How to Cite AI in MLA Format
Creating a reference to ChatGPT or other AI models and software
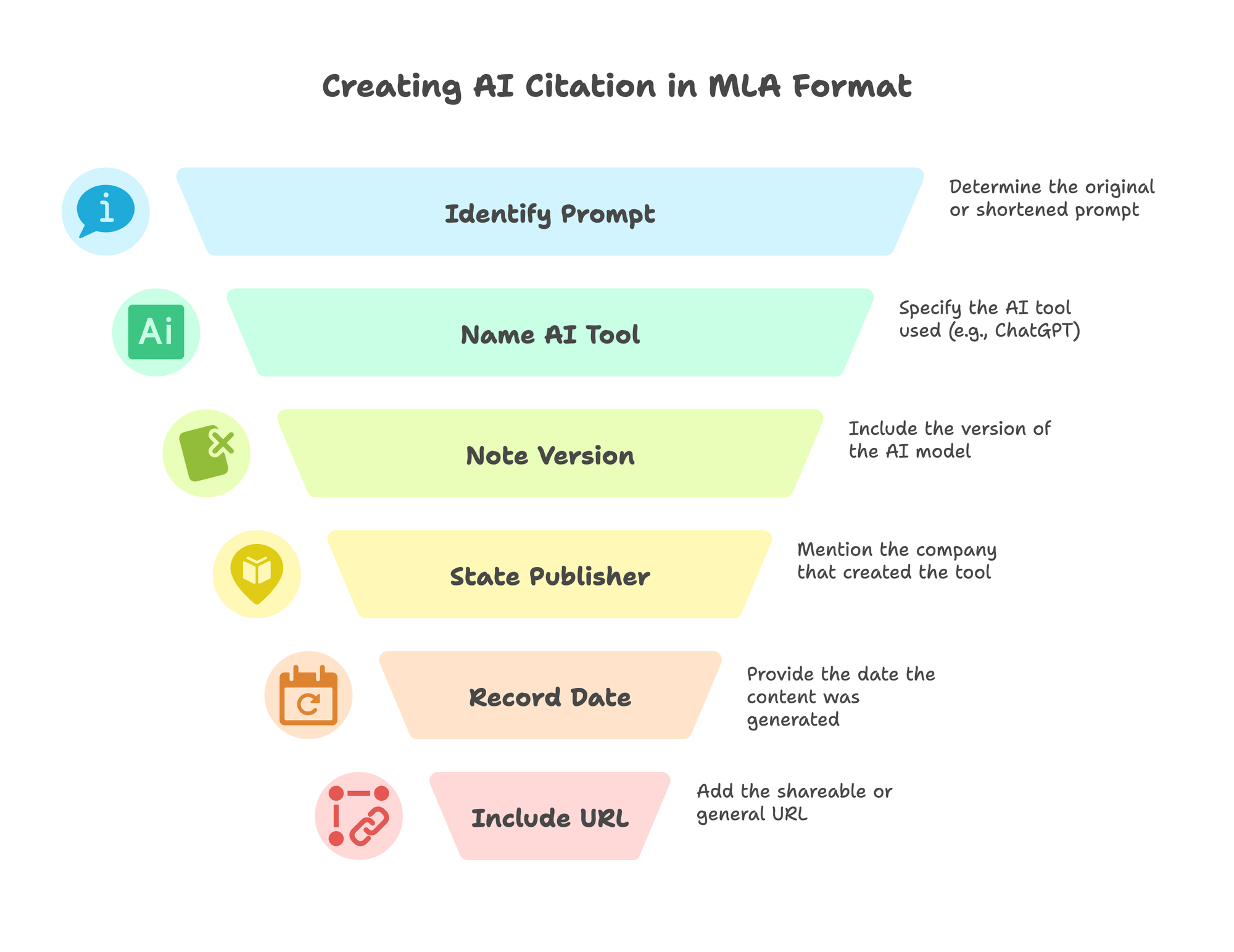
The general format to follow is:
"Description of the generated content" prompt. Title of AI Tool, Version, Publisher, Date generated, URL.
"Description of the generated content" prompt: This is the Title of Source. It should be your original prompt, or a shortened version of it, in quotation marks. Follow this with the word "prompt."
Title of AI Tool: The name of the tool (e.g., ChatGPT) is in italics as the Title of Container.
Version: The specific version of the model used (e.g., GPT-4, 8 Feb. version). If a version is not clearly listed, you can leave out this element.
Publisher: The company that made the tool (e.g., OpenAI).
Date generated: The exact date you generated the content (Day Mon. Year format).
URL: The shareable URL for the conversation, or the general URL for the tool only if a specific link is definitely not available.
How do you cite a chatbot in MLA?
When citing a chatbot like Claude, Gemini, or any other generative model, you follow the same pattern: begin with your description, then list the tool, version, company, and date. The description becomes the title in your Works Cited entry and the phrase you use in your in-text citation.
This means your in-text citation will reference your description in parentheses, as you would cite a source with no author: (“Analysis of Act II themes”). Since MLA prioritizes adaptability, you can adjust the level of detail as required.
The key is consistency: whatever description you choose in the Works Cited should match what appears in your in-text citation. By grounding your citation in a firm description and transparent metadata, you give your reader everything they need to understand how AI contributed to your work.
How to Cite AI in MLA: Full Citations
To make these guidelines easier to follow, it helps to see how they work with real student assignments. Here are examples drawn from three sample essay topics:
- How should judges be appointed?
- How do coral reefs protect lives and property?
- When, if ever, is forgiveness wrong?
Each example follows MLA’s structure for AI: a brief description of the output, the tool name, version, company, date, and (if available) a link to the chat transcript.
Example 1: Essay on judicial appointments (ChatGPT)
If you asked ChatGPT to outline how judges are selected in different countries and incorporated part of that explanation into your essay, your Works Cited entry would look like:
Works Cited entry:“Summary of judicial appointment methods” prompt. ChatGPT, GPT-3.5, OpenAI, 8 Feb. 2025, chat.openai.com/g/38239493.
In-text citation:(“Summary of judicial appointment methods”)
Example 2: Essay on coral reefs and coastal protection (Claude)
If you used Claude to explain how coral reefs reduce wave energy or protect coastal communities, your MLA citation would reflect the tool and the version you used.
Works Cited entry:“Explanation of how coral reefs reduce storm impact” prompt. Claude, 3.2, Anthropic, 8 Feb. 2025, claude.ai/coral-reefs.
In-text citation:(“Explanation of how coral reefs reduce storm impact”)
Example 3: Essay on the ethics of forgiveness (Gemini)
If you asked Gemini to summarize philosophical arguments about whether forgiveness can ever be morally wrong then your MLA citation would look like:
Works Cited entry:“Overview of ethical arguments about forgiveness” prompt. Gemini, version 2.0, Google, 8 Feb. 2025, https://gemini.google.com/app/c6f3e8ab96872b.
In-text citation:(“Overview of ethical arguments about forgiveness”)
How to Cite AI in MLA: Parenthetical Citations
Parenthetical citations for AI in MLA are straightforward once you remember one rule: because AI outputs have no author, the citation begins with the short description you used as the title in your Works Cited entry.
Unlike traditional MLA citations, there are no page numbers and no author names to reference. Instead, the citation points back to the descriptive title you created for the AI output.
Here are examples from the sample essay topics to show how this works.
Example 1: Judicial appointments essay (ChatGPT)
If you used ChatGPT to explain how merit-based or commission-based systems work and included that material in your paragraph, the corresponding in-text citation would simply reference your shortened description:
In-text citation:(“Summary of judicial appointment methods”)
This points your reader directly to the same description used in your Works Cited entry.
Example 2: Coral reefs and coastal protection essay (Claude)
If you paraphrased Claude’s explanation of how coral reefs reduce wave energy or buffer communities from storms, your parenthetical citation would look like:
In-text citation:(“Explanation of how coral reefs reduce storm impact”)
Since the title functions as the identifier, MLA doesn’t add tool names or versions inside parentheses.
Example 3: Ethics of forgiveness essay (Gemini)
If you incorporated a summary from Gemini about cases where forgiveness might conflict with justice or accountability, your parenthetical citation would be:
In-text citation:(“Overview of ethical arguments about forgiveness”)
Again, the aim is clarity. The reader sees a clean reference that matches the first element of the Works Cited entry.
Parenthetical Citations: Do/Don’t Guide
How to cite AI-generated images in MLA
MLA treats AI-generated images differently from traditional artwork as the image doesn’t have a human creator in the typical sense. Instead, you are considered the creator of the image, and the AI tool functions as the method you used to produce it. That means the citation focuses on your prompt and the details of the tool, instead of assigning authorship to the model itself.
The prompt functions as the title, the model and version function as the tool, and the date shows when the image was produced. This is why captions and Works Cited entries both emphasize what the image shows rather than who “made” it.
You’ll need two things:
- A caption beneath the image (following MLA figure guidelines)
- A Works Cited entry describing how the image was generated
This approach shows your process while acknowledging that the image can’t be retrieved or verified in the same way a published artwork can.
1. Caption for an AI-generated image (MLA format)
The caption begins with Fig. X, followed by a brief description of the image and a note about how it was created.
Example (coral reefs topic):Fig. 1. AI-generated image of a coral reef acting as a natural storm barrier, created using DALL·E on 8 Feb. 2025.
Example (judicial appointments topic):Fig. 1. AI-generated diagram comparing judicial appointment systems, created using ChatGPT-4o on 8 Feb. 2025.
2. Works Cited entry for an AI-generated image
The Works Cited entry follows the same principle as AI text: begin with a short description of the output, then list the tool, version, company, date, and shareable link.
Template:“Description of image” prompt. Name of AI tool, Version, Company, Date, URL (if available). AI-generated image.
Example 1: Coral reefs essay (DALL·E)
If you asked DALL·E to create an illustration showing how coral reefs reduce storm impact, your Works Cited entry might look like:
Works Cited entry:“Coral reef storm-barrier illustration” prompt. DALL·E, version 3, OpenAI, 8 Feb. 2025, labs.openai.com. AI-generated image.
Example 2: Judicial appointments essay (ChatGPT image generator)
If your essay includes a diagram generated through ChatGPT’s image capabilities:
Works Cited entry:“Diagram of judicial appointment models” prompt. ChatGPT Image Generator, GPT-4.1, OpenAI, 8 Feb. 2025, chat.openai.com. AI-generated image.
Example 3: Ethics of forgiveness essay (Gemini image model)
If you used Gemini to create a conceptual illustration related to forgiveness:
Works Cited entry:“Conceptual illustration of forgiveness boundaries” prompt. Gemini Image, version 2.0, Google, 8 Feb. 2025, gemini.google.com. AI-generated image.
Other common questions about citing ChatGPT and AI
Do I have to cite AI if I paraphrased it?
Yes, as paraphrasing still counts as using AI-generated content. If Claude helped you rephrase a description of how coral reefs protect coastlines, your reader needs to know that the idea originated in an AI-generated explanation, even if you rewrote it in your own words.
Do I need a URL when citing AI?
Only if you have a shareable link to the specific transcript. MLA prefers a transcript link when available because it allows readers to understand the context of the AI output.
Should I include the AI model in the in-text citation?
No. Tool names, versions, manufacturers, and dates belong in the Works Cited entry. Your in-text citation should use only the short description, such as: (“Overview of ethical arguments about forgiveness”).
Conclusion
When we break it down, citing AI in MLA format is a repeatable process that becomes easier the more you get into the habit of doing it. Key things to remember are to include a shareable link if you have one, and to be upfront about how AI contributed to your work, as the MLA system is all about traceability.
As José Antonio Bowen, author of Teaching with AI, says, "I do though think it will shift, as no one acknowledges a thesaurus or spell checker any more." While citation norms might change as AI becomes more common in workflows, for now, it’s important to cite AI when you’ve used it as a source. If you’re in doubt, make sure to cite: it’s better to over-communicate than to leave out where your research material came from.
Note: The views expressed by the individuals quoted are their own and do not necessarily reflect the views or official positions of the educational institutions or professional organizations with which they are affiliated.


