How AI Content Detectors Work To Check For AI
Learn how AI content detectors spot the difference between AI and human writing – with a simple breakdown of the cutting-edge technology behind the tools.

By 2026, it’s estimated that a whopping 90% of online content could be AI-generated. It’s never been more important to be able to differentiate between human-generated and AI-generated content – but how do AI content detectors actually work? Here, we uncover the science behind these sophisticated systems.
Key takeaways
- AI detectors work by analyzing how text is written, its wording, rhythm, and structure, to figure out whether it was created by a human or an AI.
- They look for patterns like how predictable the writing is (called perplexity) and how much it varies in length and tone (i.e. natural language processing) to spot the difference between natural human expression and AI’s more uniform style.
- People use these tools in schools, workplaces, media, and recruitment to check that content is authentic and genuinely reflects human effort and voice.
- No detector is perfect as they can make mistakes, especially with short, edited, or mixed pieces of writing, so human judgment is always part of the process.
- Looking ahead, detection tools are becoming more advanced, expanding beyond text to analyze images and videos, with the goal of keeping creativity transparent and human originality front and center.
What are AI content detectors?
AI content detectors are tools that analyse text to figure out if it was written by a human or an AI system. They use algorithms to look at how words are used, how sentences are structured, and what the text means, comparing it to large datasets of known AI-generated and human-written content.
If you’re wondering “how do AI detectors work,” it starts here: they look at linguistic and statistical patterns to assess how predictable or varied a piece of writing is.
At GPTZero, our detection model has undergone third-party validation by the Penn State AI Research Lab (2024). Our work has also been cited in The New York Times, Forbes, and CNN, reflecting its recognized role in shaping responsible AI detection standards.
How do AI detectors work?
Most detectors, including GPTZero, use a combination of linguistics, deep learning, and interpretability techniques, meaning our model doesn’t just classify results but also explains why. This “explainability” principle aligns with emerging transparency guidelines from the OECD and UNESCO on responsible AI.
Many AI content detectors rely on the same techniques AI models like ChatGPT use to create language, including machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP).
Machine learning (ML)
Machine learning is about recognizing patterns – the more text is analyzed, the more easily the tools can pick up the subtle differences between AI-generated and human-generated content.
Our ML pipeline is continually updated with outputs from the latest AI models, including GPT-4o, Claude 3, and Gemini 1.5, ensuring reliable detection of next-generation systems. Machine learning drives predictive analysis, which is critical for measuring perplexity (which we’ll get to later) – a key indicator of AI-generated text.
Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing is about the nuances of language, and helps AI detectors gauge the context and syntax of the text it is analyzing. AI can create grammatically correct sentences but tends to struggle with being creative, subtle, and adding depth of meaning (which humans naturally use in their writing).
Classifiers and Embeddings
Within these broad categories of ML and NLP, classifiers and embeddings play important roles in the detection process. Classifiers place text into groups depending on the patterns they have learned: much like teaching someone to sort fruits based on characteristics they’ve learned, but applied to language.
Embeddings represent words or phrases as vectors, which create a ‘map’ of language – this allows AI detectors to analyze semantic coherence.
A potential alternative: Watermarks
Another approach researchers have explored is AI watermarks, which are hidden signals embedded in AI-generated text during the creation process that would make it identifiable. While watermarking remains promising, most experts (including OpenAI and Anthropic) acknowledge it’s not yet a reliable or industry-standard solution due to tampering risks. The main thing holding it back from being implemented is that watermarks can be removed, edited or forged fairly easily.
Methods AI detectors use
AI detectors rely on a mix of linguistic and technical cues and analyze how natural or predictable the text feels, looking at sentence structure and variation. AI-generated writing often follows consistent patterns and repeats familiar phrases, while human writing tends to surprise the reader with more creativity and originality.
Some systems scan for hidden digital “watermarks” or metadata traces embedded during text generation, though these can easily disappear through editing or translation. Others compare text against large databases of known AI outputs to identify familiar patterns, but this method becomes less effective as AI models grow more advanced and diverse in their language capabilities.
Key techniques in AI content detection
GPTZero was one of the first AI detectors to pioneer the idea of using "perplexity" and "burstiness" to evaluate writing. Since then, we have evolved our model beyond just these two factors, into a multilayered system with seven components to determine if text was written by AI – but it’s worth looking at where the model began.
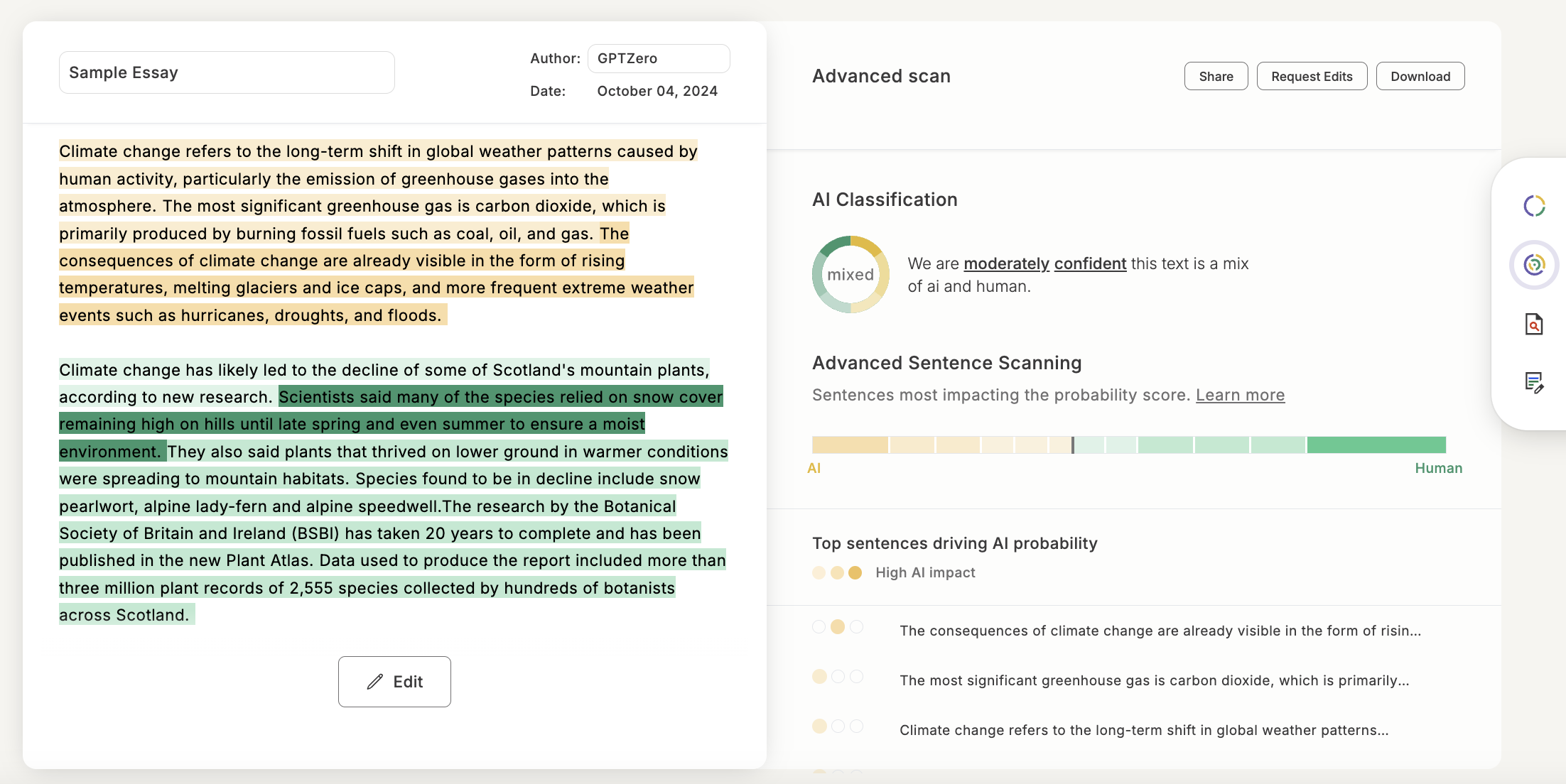
Perplexity
Perplexity is like a surprise meter when it comes to AI content detectors. The higher the perplexity, the more ‘surprised’ the detector is by the text it is seeing – as unexpected or unusual words or sentence structures tend to raise the perplexity score. If the text is ranked to have higher perplexity, it is more likely to be created by a human. If the text is too predictable, it’s likely to be AI authorship.
Burstiness
Burstiness is a measure of how much the perplexity varies over the entire document – and is more about how the text flows. While human writing has a rhythm of short and long phrases, mixing up both simple and complex sentences, AI can often be a lot more predictable. Which means its sentences tend to be fairly uniform.
This means AI generators often veer towards lower burstiness and create more monotonous text – repeating certain words or phrases too frequently because they've seen them appear often in their training data.
The interaction between perplexity and burstiness
While perplexity is about the individual surprises of specific words and phrases, burstiness is more about the overall rhythm of a piece.
A text with high burstiness can lead to higher perplexity as this is like a curveball to AI, with sudden shifts in sentence length making it harder for the AI to predict what comes next. But low burstiness often means lower perplexity – uniform sentences mean that AI has an easier time spotting the pattern and predicting the next words.
AI content detectors look for a balance of perplexity and burstiness that mimic the way humans naturally write and speak. Too much of either perplexity or burstiness can be a red flag.
Why do AI detectors matter
As AI tools become more user-friendly and more of the world starts to engage with them, there has been a growing flood of AI-generated content, prompting concern over content integrity and quality. In fact, experts say that as much as 90 percent of online content could be AI-generated by 2026.
AI content detectors have become more popular recently across industries for several key reasons around maintaining standards around authenticity and trust:
Students
A Pew Research survey last year showed that 26 percent of teenagers reported using ChatGPT for schoolwork, which was double the rate of the previous year. With students becoming more wary of being accused of using AI in their work, more are using AI detectors to proactively demonstrate the originality of their work before they hand it in.
Education institutions
Schools, colleges and universities use AI detectors to uphold academic integrity. They help educators find out whether students have used certain AI tools too heavily, which makes sure that submitted work is an honest reflection of a student’s understanding of the subject area.
In this episode, “Teachers vs Students: Is AI Destroying Education?”, students and teachers sat face-to-face to read passages aloud, guessed which ones were written by humans and which were written by AI and then checked their instincts using GPTZero.
Businesses
In professional settings, AI tools are being used to create content at scale for websites, blogs and social media, as well as for general marketing materials and internal communications. Many companies now include AI detection in editorial workflows to comply with transparency requirements set by Google’s 2025 Search Quality Rater Guidelines.
Recruiters
Recruiters use AI detectors to make sure that application materials, especially cover letters and personal statements, are actually written by the candidates themselves. This helps with fair evaluation and prevents AI-written submissions from slipping through screening, which only causes an unnecessary extra workload to sift through.
Politics, journalism and social media
With the rise of deepfakes and the spread of misinformation, AI detectors are used to grade the integrity of news and make sure false content is not mistaken for genuine information. This is particularly crucial during election cycles, when content can influence public opinion and threaten the democratic process.
Web content writers and copywriters
Writers who use AI tools to support their drafting process often run their work through AI detectors before publishing. This helps them avoid being flagged by search engines or algorithms, and ensures that their content is recognized as human-led and original.
Forensic analysts
In legal and investigative contexts, forensic analysts use AI detectors to verify the origin of written material. These tools can help determine whether disputed documents were created by humans or AI systems, supporting the integrity of evidence.
AI trainers and researchers
Developers and researchers use AI detectors to study how detection systems work and to train future AI models more responsibly. By understanding what makes writing detectable, they can design new models that promote transparency and ethical AI development.
Building a custom AI model to detect AI
As AI evolves rapidly to learn how to sound more human, AI detectors like GPTZero are also evolving to keep up with the new models. We’ve built a custom model that trains on human and AI text from the latest models to constantly evaluate for key differences between AI and human text beyond just perplexity and burstiness.
These days, our model also includes features like our Advanced scan, a sentence-by-sentence classification model; Internet Text Search, which checks if text has been found to exist in text and internet archives; and a shield that defends against other tools looking to exploit AI detectors. We combine these methods with even more dynamic ways to keep up with AI and the latest attempts to bypass AI detection.
We also collaborate with educational institutions through our 1,300-member Teacher Ambassador community to refine these tools in real-world settings.

How reliable are AI detectors?
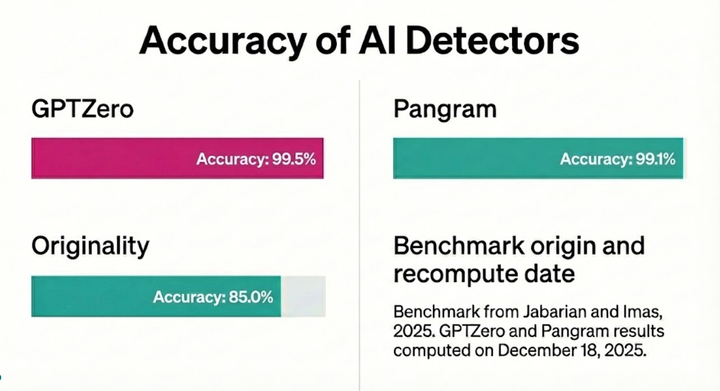
No tool can honestly claim to be 100% accurate. Instead, the goal for any good AI tool should be to have the highest accuracy rate with the lowest rate of false positives and false negatives. GPTZero has a 99% accuracy rate and 1% false positive rate when detecting AI versus human samples.
The real challenge is in detecting mixed documents that contain both AI-generated and human-written content. GPTZero is much better than our competitors at detecting mixed documents, with a 96.5% accuracy rate. When AI-generated content has been edited or blended with human writing, identification becomes even more complex. Detectors can also struggle with unconventional or highly creative writing styles that fall outside the typical training data, leading to occasional uncertainty.
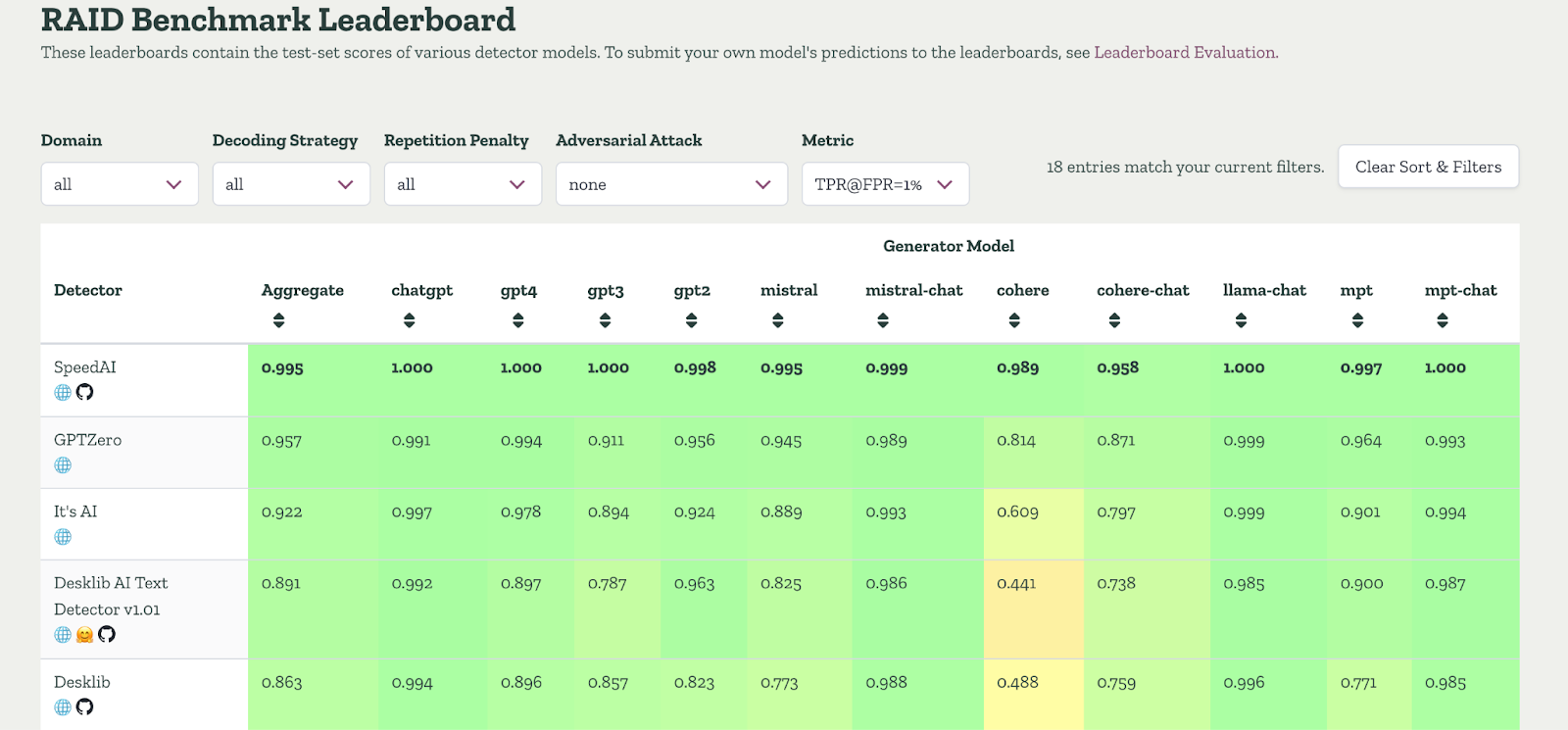
However, GPTZero has also once again proven itself as the most accurate detector in North America, according to independent third-party benchmarks from RAID, a comprehensive dataset of 672,000 texts spanning 11 domains, 12 LLMs, and 12 adversarial attacks. On RAID, GPTZero correctly identified 95.7% of AI-written text while misclassifying only 1% of human writing, with accuracy exceeding 99% on modern models like GPT-4. Unlike competitors such as Copyleaks, Originality, and Pangram, GPTZero’s performance remained consistent even under adversarial conditions like paraphrasing or synonym swaps.
Essentially, several factors influence how reliable AI detectors can be. Short passages are more difficult to analyze because they offer fewer linguistic patterns for the model to evaluate, while longer texts provide more context and consistency for comparison. As AI systems evolve, their writing becomes increasingly human-like, making it harder for detectors to spot clear differences.
GPTZero is trained on millions of documents spanning various domains of writing including creating writing, scientific writing, blogs, news articles, and more. We test our models on a never-before-seen set of human and AI articles from a section of our large-scale dataset, in addition to a smaller set of challenging articles that are outside its training distribution.
AI detectors vs. plagiarism checkers
AI detectors look for how text was written; plagiarism checkers look for where text came from. This distinction is recognised in the International Center for Academic Integrity’s 2024 guidelines, which recommend using both together.
AI detectors look at the text’s structure and word choice and overall style to see whether it was created by artificial intelligence or a human – and involves advanced algorithms and linguistic analysis.
Meanwhile, plagiarism checkers are more straightforward and are essentially looking to match the text, and compare the writing against a broad data set of existing writing. When they spot similarities or matches, they will flag this as potential plagiarism.
Basically, AI detectors exist to make sure the content is genuinely written by a human, while plagiarism checkers exist to confirm it is not copied from existing sources. However, neither type of tool is perfect and in both cases, results should be evaluated critically and used as input sources rather than singular and definitive judges.
AI image and video detectors
While text-based AI detectors analyze words and sentence patterns, image and video detectors focus on identifying the visual fingerprints of generative models. These tools examine subtle visual clues like uneven lighting or texture glitches to check authenticity.
Many also use deep learning to compare visual features against known datasets of synthetic and authentic images. For instance, detectors can spot irregularities in reflections, skin textures, or background details that often reveal an image’s artificial origin.
Newer systems combine visual forensics with contextual analysis, checking not just what appears in an image or clip, but how and where it was shared. This multimodal approach helps platforms and researchers assess authenticity more reliably across formats.
Limitations of AI Detectors
False positives or negatives
AI detectors work on probabilities, not absolutes – and can sometimes produce false positives or false negatives. This is because the systems are relying on algorithms which analyze patterns, and work by judging the likelihood of any given piece of content being produced by AI. Sometimes, human-written content can be mistakenly flagged as AI-generated. And similarly, AI-generated content can be mistakenly flagged as human-written. At GPTZero, we dive more into how our benchmarking works and how we arrive at our accuracy rates.
Trained on English language
Most AI detectors are trained on English language content, and can recognize structures and patterns that are commonly found in English. An AI detector might be less (or not at all) effective when analyzing multilingual content, or text in other languages. For non-English content, an AI detector might not be able to recognize specific characteristics it has been trained on, because it differs from what it is trained to recognize – making it less reliable.
Here at GPTZero, we’ve made a lot of progress in addressing language-based limitations by using a more rigorous evaluation dataset. Through refining model training and bringing in de-biasing techniques, we’ve improved GPTZero’s reliability across different language contexts.
Writing aids that increasingly use AI
Many AI detectors usually cannot tell the difference between ethically used AI assistance (with grammar tools such as Grammarly) and completely AI-generated content. Some systems cannot always differentiate between someone using AI for minor edits like grammar corrections, or leaning on AI to generate the entire text.
GPTZero has trained our models to account for this, and GPTZero’s “Paraphraser Shield” differentiates between light editing tools (like Grammarly) and full AI rewriting.
Difficulty detecting advanced AI models
As AI systems become more sophisticated, their writing is becoming nearly indistinguishable from human text. Newer models are trained on massive, diverse datasets and can mimic natural rhythm, tone, and even emotional nuance with surprising accuracy. This makes it increasingly difficult for traditional detection methods to keep up, as the usual linguistic clues that once gave AI away, like repetitive phrasing or overly smooth grammar, are now often much less obvious.
No such thing as definitive proof
AI detectors work on probabilities and so a high AI-likelihood score means the text shares patterns common to AI writing. That is very different from being able to say that it was definitely produced by an AI. AI detectors, in this sense, cannot provide absolute certainty. This is why in practice, these tools are best used as part of a wider review process, alongside human judgment and other verification methods.
Why over reliance is risky
When used alone, AI detectors can lead to unfair outcomes, like wrongly flagged student essays or errors in content moderation. The most responsible approach is to combine them with other verification methods such as plagiarism checks and writing history analysis (like GPTZero’s Writing Report).
Best practices for using AI detectors
With all of the above in mind, AI content detectors should be treated as tools in a broader strategy when it comes to gauging content integrity, as opposed to standalone judges of content quality. To use AI detectors effectively, we need to recognize their limitations and bring in human judgment for the specific context in which the content is being created.
The below outlines the steps you can take (if you work in education, we also recommend checking out our post on How Should Educators Approach AI and Academic Integrity?).
Acknowledge the limitations
There is no AI detector in the world that is flawless. These tools can sometimes misclassify text, leading to false positives or false negatives, and their findings should be treated as one piece of evidence, a signal to investigate further, not a final verdict.
Cross-check with multiple tools
Relying on a single detector can create blind spots and can also cause over-reliance on that tool. It’s a great idea to use more than one AI detection tool as this gives a broader, more reliable picture and helps minimize the risk of error.
Learn to recognize AI writing patterns
AI-generated text often follows predictable rhythms and repeats certain words or phrases. There is also no nuance. Understanding these tendencies makes it easier to interpret detector results and identify when something truly feels machine-written.
Consider context and intent
A flagged result should always prompt a closer look. Compare the writing to the person’s usual tone, phrasing, and clarity. If the style feels noticeably different, AI detection can be a helpful starting point for review but never the sole determining factor in a decision.
Be transparent about detection
Whether in academic or professional settings, it’s getting ever more important to explain how AI detection fits into your review process. Setting clear standards for when and how results are used helps build trust and prevents overreliance on automation. (If you need help setting a policy for your institution, you might find this guide useful.)
Use AI detection as part of a wider originality check
AI detection works best alongside other verification tools such as plagiarism checkers and citation validation. Together, these provide a fuller picture of how someone has completed their work and overall provides a more holistic approach to content evaluation.
The bottom line is that these tools are not ultimate authorities. They should complement human judgment, especially in situations where false positives or negatives can have long-reaching consequences. The central way to use AI detectors responsibly is to take a balanced approach that prioritizes fairness above convenience.
Future of AI detection technology
As generative AI keeps progressing, so too do the tools that are designed to detect it. The next generation of detectors will go beyond text and also be able to analyze multimedia to spot when something has been created or edited by AI. Researchers are already working on systems that can adapt in real time as new models appear, instead of relying on old benchmarks that quickly become outdated.
We’re already seeing promising research around dynamic detection models that can adapt to new AI systems in real time, rather than relying on static benchmarks. In the near future, the most effective tools will be part of helping to build systems where transparency and attribution are baked in from the start, by design.
Conclusion
AI content detectors are more crucial than ever as they help educators maintain academic honesty and businesses preserve trust, when automation is becoming more prevalent. Like all tools, they are best when used thoughtfully, as part of a broader commitment to transparency.
In our opinion, the best AI detectors are built around safeguarding what’s authentic and supporting a digital environment where originality still matters, or, in other words, preserving what’s human.
FAQ
How does GPTZero’s AI detection work?
GPTZero analyzes text using multiple layers of linguistic and statistical analysis, including metrics like perplexity, burstiness, and semantic coherence. It classifies writing at both the document and sentence level to determine whether it was likely written by a human or an AI model.
Why do AI detectors sometimes flag human-written content?
AI detectors assess probabilities. If a piece of writing follows patterns that resemble AI such as uniform sentence lengths or repetitive phrasing, it may be flagged even if it was human-written. Reviewing results in context helps avoid misinterpretation.
Should I rely on AI detectors to verify content authenticity?
No single detector should be treated as a final authority. They’re most effective when combined with human judgment and other verification methods such as plagiarism checkers and writing history reports.
What are the rules on how to cite AI?
Citing AI varies by institution and publication, but most guidelines recommend acknowledging when tools like ChatGPT or Claude have been used to generate ideas or text. Always check the citation policy of your organization or publisher.
Can you detect AI-written code?
Detecting AI-generated code follows similar principles but requires specialized tools trained on programming languages.